Included under terms of UK Non-commercial Government License.
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Galdas P, Darwin Z, Fell J, et al. A systematic review and metaethnography to identify how effective, cost-effective, accessible and acceptable self-management support interventions are for men with long-term conditions (SELF-MAN). Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2015 Aug. (Health Services and Delivery Research, No. 3.34.)

A systematic review and metaethnography to identify how effective, cost-effective, accessible and acceptable self-management support interventions are for men with long-term conditions (SELF-MAN).
Show detailsThe objective of the qualitative metaethnography was to systematically identify experiences of, and perceptions of, interventions or specific activities aimed at supporting or promoting self-management of LTCs among men of differing age, ethnicity and socioeconomic background.
A summary of the methods used in the metaethnography is provided in Appendix 3, using the enhancing transparency in reporting the synthesis of qualitative research (ENTREQ) reporting standards for qualitative evidence synthesis, developed by Tong et al.93
The evidence synthesis was conducted using a metaethnography approach originally described by Noblit and Hare.94 This approach was chosen because of its emphasis on conceptual development and generating new insights (i.e. being interpretive rather than integrative94) and because it is compatible with synthesising all types of qualitative research.95
Metaethnography involves seven stages: getting started, deciding what is relevant, reading the studies, determining how studies are related to each other, translating studies into each other, synthesising translations and expressing the synthesis;94 these seven, often overlapping, stages are depicted in Figure 7.
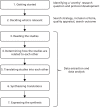
FIGURE 7
Seven steps of metaethnography.
Step 1: getting started
The first stage involved identifying a ‘worthy’ research question and one that could be addressed through qualitative evidence synthesis.94 This stage took place in developing the original funding application for the current review and its justification is presented in Chapter 1.
Step 2: deciding what is relevant
The second stage, ‘deciding what is relevant’, was viewed as comprising the search strategy, inclusion criteria and quality appraisal, consistent with the experiences of Atkins et al.96 These are presented next, before steps 3–7 are described in the section Data extraction strategy and data analysis.
Search methods
Search strategy
A comprehensive electronic search strategy (Appendix 4) was developed in liaison with information specialists. It sought to identify all available studies, rather than using purposive sampling to identify all available concepts. Five electronic databases were searched in July 2013 [Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), EMBASE, MEDLINE, PsycINFO and Social Science Citation Index].
Because of challenges with methodological indexing of qualitative research,97 the electronic search was complemented by checking reference lists, and using an adapted strategy published elsewhere98 that includes ‘thesaurus terms’ (keywords indexed in electronic databases, e.g. ‘Qualitative Research’), ‘free text terms’ (commonly used research methodology terms searched for in the titles, abstracts and keywords) and ‘broad-based terms’ (i.e. the broad free-text terms ‘qualitative’, ‘findings’ and ‘interview$’ and the thesaurus term ‘Interviews’). Terms relating to gender were combined with other terms to narrow the search and increase the precision of the strategy (e.g. ‘men’, ‘male’, ‘masculine$’, ‘gender’, ‘sex difference$’, ‘sex factors’).
Study selection: study screening methods and inclusion criteria
Records were initially screened by one reviewer (ZD) on the basis of the title and abstract. Decisions were recorded in EndNote X7.0.2 (Thomson Reuters, CA, USA), a reference management database. All articles identified as potentially eligible for inclusion were obtained in full. Attempts were made to identify and obtain published findings for unpublished literature that was otherwise eligible, for example doctoral theses or conference proceedings.
The full-text literature was screened independently by two reviewers (ZD and PG) using the inclusion criteria listed in Table 5. Studies that explored the experiences of men alone, or included a clear and explicit comparison between men and women, were included. Studies which focused on self-management experiences of people with LTCs more generally (i.e. did not consider experiences of, or perceptions of, a self-management support intervention or activity) were excluded. The approach to screening was inclusive; for example, studies where the qualitative findings were limited (e.g. Iredale et al.,99 Ramachandra et al.,100 Smith et al.101) and mixed-sex studies with limited findings on gender comparisons (e.g. Barlow et al.102,103) were retained in case they contributed to the synthesis.
TABLE 5
Screening criteria: qualitative
Classification of self-management interventions and support activities in the qualitative evidence synthesis
The original study protocol sought to code self-management interventions and support activities using the most up-to-date version of the taxonomy of BCT.104–106 As in the quantitative review (see Chapter 2, Coding interventions for analysis), we found that the level of detail reported on self-management interventions or activities in the qualitative literature was limited in detail, precision and consistency, making coding with the BCT taxonomy unfeasible.
Most of the qualitative literature did not focus on behaviour change per se or seek to address men’s views and experiences of behaviour change techniques; for example, some papers were concerned with the dynamics of social support groups, or the use of other self-management support and information. The BCT taxonomy is applicable to only studies that are judged as targeting behaviour change; we were therefore limited to ‘lifestyle’ and ‘psychological’ studies. Only a minority of the studies (n = 13) provided sufficient information on interventions to allow even rudimentary coding with the BCT taxonomy, and these are presented in Appendix 5. Issues around application of the BCT taxonomy are returned to in the discussion chapter (see Chapter 6).
The lack of detail reported in the qualitative literature also made it unfeasible to classify interventions using the system developed for the quantitative review. Whereas the quantitative review concerned trials of specific interventions, approximately half of the studies in the qualitative review99,101,107–130 included more than one intervention or activity (e.g. ‘any cancer support group’).
We therefore developed a broad system for classifying interventions and support activities that offered a pragmatic way to group studies and make the analysis process more manageable. The categories are shown in Table 6.
TABLE 6
Categories and descriptions of self-management interventions and support activities in the qualitative evidence synthesis
Quality assessment strategy
The purpose of quality appraisal in the review was to provide descriptive information on the quality of the included studies rather than as a basis for inclusion. We considered that studies of weaker quality either would not contribute or would contribute only minimally to the final synthesis.94,131 We therefore chose not to use design-specific appraisal tools (which the original protocol stated we would) because we placed emphasis on conceptual contribution, which did not require a detailed design-specific appraisal of methodological quality. With that in mind, we used the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) tool.132
The CASP tool comprises 10 checklist-style questions (see Appendix 6) for assessing the quality of various domains (including aims, design, methods, data analysis, interpretation, findings and value of the research). Because of the checklist nature of the CASP tool, we developed some additional questions informed by other metaethnography studies96,131 that enabled us to extract and record more detailed narrative summaries of the main strengths, limitations and concerns of each study (see Appendix 7).
The CASP tool was used in the light of the experiences reported by other researchers who recommended that, despite rather low inter-rater agreement, such an approach ‘encourag[es] the reviewers to read the papers carefully and systematically, and serves as a reminder to treat the papers as data for the synthesis’ (p. 44).131
Its focus is on procedural aspects of the conduct of the research rather than the insights offered.133 The quality appraisal (which focused on methodological quality) did not form part of the inclusion criteria because, as recognised by Campbell et al.,131 it is conceptual quality that is most important for evidence synthesis and it is the process of synthesis that judges the ‘worth’ of studies, with conceptually limited studies making a limited contribution.94 Additionally, it is acknowledged that agreement is often slight, with low reproducibility.131,133 Appraisal was conducted by two reviewers independently (ZD and PG), with discrepancies resolved through discussion.
Search outcome
The electronic search strategy identified 6330 unique references. Screening based on title and abstract identified 149 papers for full-text screening. Dual screening of these full-text articles identified 34 studies (reported in 38 papers) to be included in the review. Reasons for excluding the remaining 111 articles are shown in Table 7.
TABLE 7
Reasons for exclusion of full-text articles
Inter-rater agreement on the decision to include was 88.6%. The majority of disagreements (n = 17) concerned the definition of self-management intervention or activity. Having discussed the 17 disagreements, we agreed that five studies on which there was disagreement would be included.100,103,110,116,134
An additional four studies were identified through reference checks and efforts to locate published literature linked to unpublished work identified through the electronic search.111,112,135,136 An additional two papers (women only), although individually ineligible, were located as ‘linked papers’ for two of the original 34 studies,114,120 giving a total of 38 studies (reported in 44 papers), as shown in Figure 8.

FIGURE 8
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses flow diagram for the qualitative review.
Data extraction strategy and data analysis
The lead reviewer (ZD) extracted all papers using data extraction forms previously tested and refined through a pilot study of four papers. All study details (including aim, participant details, methodology, method of data collection and analysis) were extracted into Microsoft Excel® version 14 (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA) and checked by a second reviewer (PG). Extraction and analysis of study findings was undertaken by a group of coreviewers within the research team (ZD, PG, LK, CB, KM, KH) and followed steps 3–7 of the metaethnography process described by Noblit and Hare.94 Despite being numbered sequentially, these phases do not occur in a linear process.94
Step 3: reading the studies
The metaethnography process involved three levels of constructs, as described by Schutz137 and operationalised by Atkins et al.:96
- first-order: participant quotes and participant observations, while recognising that in secondary analysis these represent the participants’ views as selected by the study authors in evidencing their second-order constructs
- second-order: study authors’ themes/concepts and interpretations, also described by Noblit and Hare94 as ‘metaphors’
- third-order: our ‘interpretations of interpretations of interpretations’ (p. 35),94 based on our analysis of the first-order and second-order constructs extracted from the studies.
Each paper was read in full and copied verbatim into NVivo version 10 (QSR International, Warrington, UK) for line-by-line coding by the lead reviewer. Coding involved repeated reading and line-by-line categorising of first-order and second-order constructs, using participants’ and authors’ words wherever possible, and reading for possible third-order constructs.
Third-order constructs were developed by building second-order constructs into broader categories and themes in a framework which was revised iteratively using the hierarchical functions of the NVivo software (i.e. using ‘parent’ and ‘child’ nodes).
Rather than simply being a synthesis of the second-order constructs, third-order-constructs were derived inductively from the extracted data; this was an interpretive process that was not limited to interpretations offered by the original authors of included studies.
Coding by coreviewers (i.e. other members of the research team) was idiosyncratic but commonly involved working with printed papers, noting key ‘metaphors’ (themes, concepts and ideas) in the margins and highlighting first-order and second-order evidence that supported the coreviewers’ interpretations. The lead reviewer, ZD, met with each coreviewer to discuss/debrief coding decisions and ensure the credibility (i.e. the congruence of coding decisions with the original author interpretations) of the overall analytical process.
Step 4: determining how the studies are related
To offer a ‘way in’ to the synthesis, we adopted a similar approach to that of Campbell et al.:131 initially grouping studies by the broad categories of self-management intervention and support activity shown in Table 6. Each coreviewer was allocated one or more category of studies to analyse. The lead reviewer then read each category of studies in the following order: face-to-face group support, online support, online information, information, psychological, lifestyle and ‘various’; within this, she read the studies in alphabetical order of first author rather than nominating ‘key’ papers. All included papers were analysed, rather than reading until saturation of concepts.
The lead reviewer and coreviewer independently completed matrices to report the second-order constructs and emerging third-order constructs for each paper (which for the lead reviewer were based on a more comprehensive line-by-line coding using NVivo). This facilitated the juxtaposing of metaphors and/or constructs alongside each other, leading to initial assumptions about relationships between studies.
Step 5: translating studies into one another
A defining element of metaethnography is the ‘translation’ of studies into each other, whereby metaphors, together with their inter-relationships, are compared across studies. Facilitated by discussions using the matrices of second- and third-order constructs, we translated studies firstly within types of support activity and then, secondly, across types.
The lead reviewer initially developed the constructs in relation to face-to-face support (the largest category of studies) and read other categories of studies with reference to this, using a constant comparison approach to identify and refine concepts. The ‘models’ function in NVivo was used to depict relationships between third-order constructs; this helped to develop the line-of-argument synthesis, which is discussed next.
Step 6: synthesising translations
Studies can be synthesised in three ways:94
- reciprocal translation, where the findings are directly comparable
- refutational translation, where the findings are in opposition
- a line-of-argument synthesis, where both similarities and contradictions are found and translations are encompassed in one overarching interpretation that aims to discover a whole among the set of parts, uncovering aspects that may be hidden in individual studies.
Because we found similarities and contradictions, we developed a line-of-argument synthesis (rather than reciprocal or refutational translation) that encompassed four key concepts, each of which was based around a set of third-order constructs.
Step 7: expressing the synthesis
The output of the synthesis, that is communicating our third-order concepts and overarching line-of-argument synthesis, is described by Noblit and Hare94 as ‘expressing the synthesis’ (p. 29). They state that ‘the worth of any synthesis is in its comprehensibility to some audience’ (p. 82),94 emphasising the importance of communicating the synthesis effectively, being mindful of the intended audience and using concepts and language that are meaningful (and understandable). We worked to make the synthesis comprehensible by discussion with coreviewers and, critically, through involvement of the patient and public involvement (PPI) group. The synthesis is presented in Chapter 5 and will also be expressed through other dissemination activities, for example the SELF-MAN symposium (www.self-man.com), mini-manuals and journal publications.
Rigour
We undertook several steps to enhance the rigour of our analysis. Authors’ themes and interpretations (second-order constructs) were independently extracted by two reviewers, each of whom additionally suggested their own interpretations of the study findings (third-order constructs).
We were influenced by a recent Health Technology Assessment metaethnography which found multiple reviewers offered ‘broad similarities in interpretation, but differences of detail’ (p. x).131 We therefore treated the lead reviewer’s analyses as the ‘master copy’ and compared these with the coreviewers’ extractions and interpretations. Peer debriefing meetings were held between the lead reviewer and each coreviewer to discuss matrices of second-order and third-order constructs which facilitated the consideration of alternative interpretations.
The third-order constructs and line-of-argument synthesis were further refined at a full-day meeting (January 2014) attended by the lead qualitative reviewer and wider team of five coreviewers involved in coding, extraction, analysis and interpretation (PG, KH, LK, KM, CB).
We identified the need to be reflexive about our interpretations and recognised potential sources of influence on our interpretations; for example, two reviewers (PG, KH) identified having a ‘constructions of masculinity’ lens, and we agreed to focus the line-of-argument synthesis on interpretations offered by authors of studies being synthesised, rather than framing our interpretations around constructions of masculinity. We considered it a strength that the six reviewers involved reflected a wide range of backgrounds and perspectives. Although PPI colleagues were not involved in the coding process, the line-of-argument synthesis and four key concepts were discussed with the PPI group to ensure credibility.
Public and patient involvement
The SELF-MAN research team worked with a specially constituted public and patient advisory group comprising men living with one or more LTCs who were involved in either running or attending a LTC support group in the north of England. Members were recruited via the research team’s existing networks. Stakeholders’ support groups were all condition-specific – arthritis (n = 1), diabetes (n = 1), heart failure (n = 2) and Parkinson’s disease (n = 1) – although some men lived with multiple LTCs. All stakeholders attended a welcome meeting prior to the commencement of the study to prepare them for the involvement in the research, and were provided with ongoing support and guidance by the chief investigator throughout the research process. Members were reimbursed for travel, expenses and time throughout the duration of the project (in line with current INVOLVE recommendations138).
The overarching aims of PPI in the project were, first, to help ensure that the review findings spoke to the self-management needs and priorities of men with LTCs, and, second, to ensure the development of appropriate outputs that would have benefit and relevance for service users. A recognised limitation of our group was that stakeholder representation was drawn from face-to-face group-based support interventions.
The stakeholder group met on three half-days over the course of the 12-month project. On each occasion, the group provided positive affirmation that the project was being conducted in accordance with its stated objectives. In the first two meetings, the group offered feedback and advice to the investigative team on preliminary and emerging analysis of the qualitative data throughout the research process: specifically, the development of third-order constructs and the line-of-argument synthesis. Responding to their input, we made revisions to some of our interpretations, particularly in relation to the importance of physical aspects of environments in which interventions took place. The group’s input also highlighted the need for future research to address depression as a common and often overlooked comorbidity in men (see Chapter 7, Recommendations for future research), and that they welcomed recommendations for sustainability of support groups and improving communication within groups. When considering the key outcomes to be assessed in the quantitative review, stakeholders also recommended that emphasis should be placed on quality-of-life outcome measures when considering whether or not a self-management support intervention is effective.
In the final meeting, the stakeholder group provided detailed recommendations for the content of the Self-Manual: Man’s Guide to Better Self-Management of Long Term Conditions (not yet available). It advised that the guide should be rephrased from ‘how to’ self-manage to ‘how to better’ self-manage because men may view themselves as already self-managing and therefore not identify with the former.
Six or seven stakeholders attended each meeting. The female partner of one of the men attended and contributed to discussions at each meeting. Members of the group each received reimbursement of travel expenses and a £150 honorarium for each meeting they attended. In the final meeting, the stakeholders provided feedback on their involvement in the research process overall, focusing on what was done well and what could be improved. Feedback indicated that most stakeholders had a positive experience, particularly valuing the opportunity to have their ‘voices heard’ and make a potential impact on future service delivery. Recommendations for improvements mostly centred on ensuring prompt reimbursement of expenses incurred in attending the meetings.
- Qualitative review methods - A systematic review and metaethnography to identify...Qualitative review methods - A systematic review and metaethnography to identify how effective, cost-effective, accessible and acceptable self-management support interventions are for men with long-term conditions (SELF-MAN)
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...