Clinical Description
THOC6 intellectual disability syndrome is associated with intellectual disability, distinctive facial features, microcephaly, teeth anomalies, and cardiac and renal malformations. To date, 19 individuals from 15 families with pathogenic variants in THOC6 have been identified [Boycott et al 2010, Beaulieu et al 2013, Anazi et al 2016, Casey et al 2016, Amos et al 2017, Accogli et al 2018, Nair et al 2018, Bruel et al 2019, Elmas et al 2019, Mattioli et al 2019, Gupta et al 2020, Zhang et al 2020]. The following description of the phenotypic features associated with this condition is based on these reports.
Table 2.
Features of THOC6 Intellectual Disability Syndrome
View in own window
| Feature | Proportion of Persons w/Feature | Comment |
|---|
| Intellectual disability | 19/19 | Moderate to severe |
| Facial dysmorphisms | 17/19 | |
| Microcephaly | 13/19 | |
| Teeth anomalies | 10/19 | Dental caries & dental malocclusion |
| Congenital heart defects | 9/19 | Atrial &/or ventricular septal defects |
| Short stature | 8/19 | |
| Cryptorchidism in males | 7/19 | |
| Renal malformations | 6/19 | Mainly unilateral renal agenesis |
| Ventriculomegaly 1 | Observed in at least 6 persons | |
- 1.
Ventriculomegaly may not have been assessed in all 19 reported cases in the literature so this may underestimate the actual incidence.
Developmental Delay (DD) / Intellectual Disability (ID)
Moderate-to-severe intellectual disability has been noted in all reported individuals. Most of these individuals were able to walk independently, but remained nonverbal or had very limited speech (<10 words). The oldest reported individuals are young adults.
Behavior problems. Autism spectrum disorder and motor stereotypies were described in four individuals [Accogli et al 2018, Elmas et al 2019, Mattioli et al 2019]. Obsessive compulsive behavior was observed in one individual [Amos et al 2017].
Neurologic
Most reported individuals had congenital microcephaly, predominantly 2-3 SD below the mean; 5 SD below the mean was observed in one child [Accogli et al 2018].
Epilepsy. Two affected individuals were reported to have seizures; seizure type and severity was not specified [Elmas et al 2019, Mattioli et al 2019].
Neuroimaging. Ventriculomegaly was reported prenatally in four individuals [Casey et al 2016, Accogli et al 2018, Elmas et al 2019, Mattioli et al 2019] and in six affected individuals in total [Amos et al 2017, Nair et al 2018].
One child had postnatal hydrocephalus that required ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement [
Mattioli et al 2019].
One individual had compensated supratentorial hydrocephalus due to aqueductal stenosis and was also reported to have cerebellar hypoplasia with severe vermian dysgenesis, small pons, hippocampal dysgenesis, and partial agenesis of the septum pellucidum [
Accogli et al 2018].
Corpus callosum dysgenesis was identified in five reported individuals [Amos et al 2017, Mattioli et al 2019, Bruel et al 2019, Elmas et al 2019].
Gastrointestinal Problems
Three individuals presented with feeding difficulties, two requiring feeding through a gastrostomy tube because of inadequate caloric intake by mouth [Casey et al 2016, Mattioli et al 2019]. Three individuals had anal anomalies, including anal atresia, anteriorly positioned anus, and a rectoperineal fistula [Anazi et al 2016, Amos et al 2017, Accogli et al 2018]. One affected child was reported to have had a mesenteric cyst that required surgical correction [Zhang et al 2020].
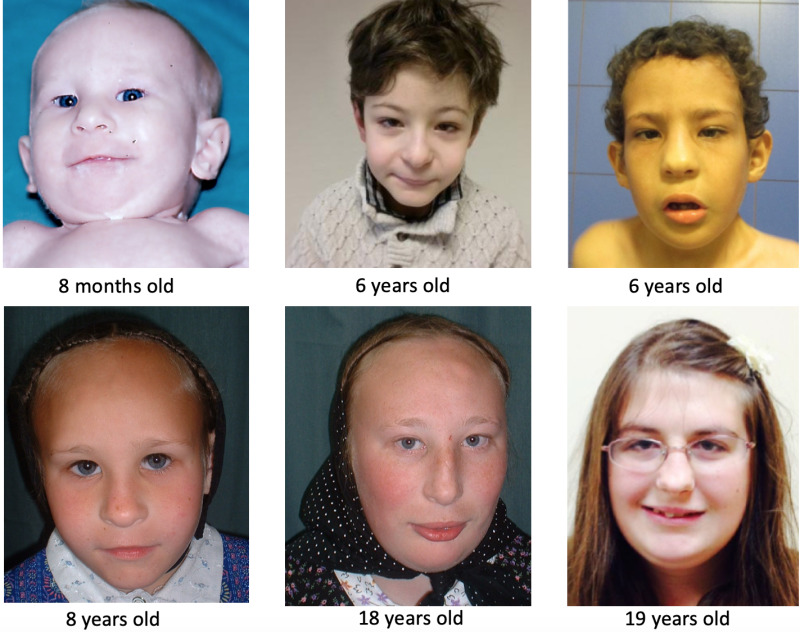
Facial Features
Dysmorphic facial features were present in most reported individuals and included the following: tall forehead, deep-set eyes, short and upslanted palpebral fissures, epicanthal folds, and long nose with low-hanging columella (). Facial features are typically not striking enough to allow a clinician to recognize the condition on this basis alone; however, the features are often recognized as consistent with this diagnosis after the diagnosis has been suggested or confirmed.
Cardiovascular Anomalies
Atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, and patent ductus arteriosus were present in eight reported individuals. A dysmorphic and mildly insufficient mitral valve was also seen in one individual [Accogli et al 2018], and pulmonary hypertension in another [Mattioli et al 2019].
Genital Anomalies / Puberty
Males
Females
Hypergonadotropic hypogonadism with primary amenorrhea requiring hormone replacement therapy was reported in another girl [
Accogli et al 2018].
Skeletal Features
Cervical hemivertebrae and multilevel vertebral segmentation defects causing a scoliosis were reported in two different individuals [Accogli et al 2018, Gupta et al 2020].
Two individuals presented with camptodactyly [Anazi et al 2016, Accogli et al 2018].
Other reported anomalies include pes planus, trigger thumb, calcaneovalgus and equinovarus deformities, cubitus valgus, congenital hip dislocation, radioulnar joint dysostosis, cervical rib, and Sprengel deformity.
Prognosis
It is unknown whether life span in THOC6 intellectual disability syndrome is shortened. The original four affected individuals are now young adults, with the oldest in their early 40s [Author, personal communication], demonstrating that survival into adulthood is possible. Since many adults with disabilities have not undergone advanced genetic testing, it is likely that adults with this condition are underrecognized and underreported.