NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Grant MD, Marbella A, Wang AT, et al. Menopausal Symptoms: Comparative Effectiveness of Therapies [Internet]. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2015 Mar. (Comparative Effectiveness Reviews, No. 147.)
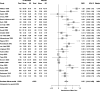
Figure G-1
Forest plot of estrogen (standard) versus placebo.
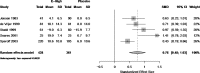
Figure G-2
Forest plot of estrogen (high) versus placebo.
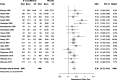
Figure G-3
Forest plot of estrogen (low/ultralow) versus placebo.

Figure G-4
Forest plot of SSRI/SNRI versus placebo.
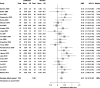
Figure G-5
Forest plot of isoflavones versus placebo.

Figure G-6
Forest plot of black cohosh versus placebo.

Figure G-7
Forest plot of ginseng versus placebo.
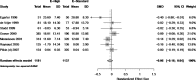
Figure G-8
Forest plot of estrogen (high) versus estrogen (standard).
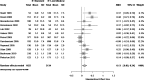
Figure G-9
Forest plot of estrogen (standard) versus estrogen (low/ultralow).
Table G-1
Network analysis excluding trials utilizing general quality of life instruments (SMDs and 95% credible intervals).
Table G-2
Quality-of-life rankings of comparative efficacy excluding trials utilizing general quality of life instruments, standard deviations, and 95% credible intervals (integer values because they arise from a distribution of integers).
- Quality of Life Supplemental Tables and Plots - Menopausal Symptoms: Comparative...Quality of Life Supplemental Tables and Plots - Menopausal Symptoms: Comparative Effectiveness of Therapies
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
