NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Sanders GD, Coeytaux R, Dolor RJ, et al. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors (ACEIs), Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists (ARBs), and Direct Renin Inhibitors for Treating Essential Hypertension: An Update [Internet]. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2011 Jun. (Comparative Effectiveness Reviews, No. 34.)

Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors (ACEIs), Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists (ARBs), and Direct Renin Inhibitors for Treating Essential Hypertension: An Update [Internet].
Show detailsWe used Comprehensive Meta-Analysis Version 2 (Borenstein M, Hedges L, Higgins J, Rothstein H. Comprehensive Meta-analysis Version 2, Biostat, Englewood NJ [2005]) to test for potential publication bias for the outcomes described below.
Diastolic Blood Pressure Reduction
We used Comprehensive Meta-Analysis to examine any potential publication bias in the studies of diastolic blood pressure reduction. The resulting funnel plot is shown in Figure H1.

Figure H1
Funnel plot for studies of diastolic blood pressure reduction.
Note that there is no asymmetry in the plot. Six studies lie to the left of the funnel, and five or six studies lie to the right. The software computed Begg and Mazumdar's correlation test for publication bias. The correlation was 0.0369 (two-tailed p-value = 0.7914). Thus there was no evidence of publication bias in this meta-analysis.
Cough In Trials Studying Diastolic Blood Pressure Reduction
We used Comprehensive Meta-Analysis to examine any potential publication bias in the RCT studies of cough in trials studying blood pressure control. The funnel plot for the studies is shown in Figure H2.
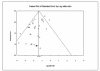
Figure H2
Funnel plot for RCTs of cough in trials studying blood pressure control.
Note that there is no asymmetry in the plot. One of the studies lies to the left of the funnel and two of the studies lie to the right. The software computed Begg and Mazumdar's correlation test for publication bias. The correlation was 0.000 (two-tailed p-value = 1.000). Thus there was absolutely no evidence of a publication bias in this meta-analysis.
Withdrawals Due to Adverse Events
We used Comprehensive Meta-Analysis to examine any potential publication bias in studies reporting withdrawals due to adverse events. The funnel plot for the studies is shown in Figure H3.

Figure H3
Funnel plot for studies reporting withdrawals due to adverse events.
Note that there is no asymmetry in the plot. Two of the studies lie to the left of the funnel, and none of the studies lies to the right. The software computed Begg and Mazumdar's correlation test for publication bias. The correlation was -0.1113 (two-tailed p-value = 0.3404). There is no evidence of a publication bias in this meta-analysis.
- Analyses of Potential Publication Bias - Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor...Analyses of Potential Publication Bias - Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors (ACEIs), Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists (ARBs), and Direct Renin Inhibitors for Treating Essential Hypertension: An Update
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...