CASRN: 117976-89-3
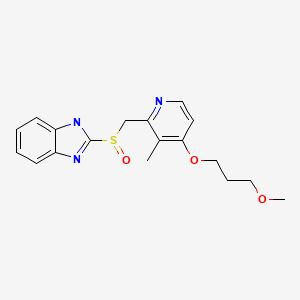
Drug Levels and Effects
Summary of Use during Lactation
Because no information is available on the use of rabeprazole during breastfeeding, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant.
Drug Levels
Maternal Levels. Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Infant Levels. Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects in Breastfed Infants
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
A retrospective claims database study in the United States found that users of proton pump inhibitors had an increased risk of gynecomastia.[1]
The Spanish pharmacovigilance system found one case of a 90-year-old man who developed gynecomastia associated with rabeprazole reported during the time period of 1982 to 2006. The reaction occurred after 32 days of therapy and resolved after discontinuation of the drug.[2]
A review article reported that a search of database from the European Pharmacovigilance Centre found 11 cases of gynecomastia, 3 cases of galactorrhea, 2 cases of breast pain and 1 case of breast enlargement associated with rabeprazole. A search of the WHO global pharmacovigilance database found 38 cases of gynecomastia, 29 cases of galactorrhea, 28 cases of breast pain and 5 cases of breast enlargement associated with rabeprazole.[3]
A woman was prescribed metronidazole 400 mg three times a day, and a combination product containing rabeprazole 20 mg and domperidone 30 mg daily for diarrhea and dyspepsia. After 3 days of treatment,
she developed bilateral galactorrhea. The combination of rabeprazole and domperidone was thought to be the cause.[4]
Alternate Drugs to Consider
Antacids, Cimetidine, Famotidine, Omeprazole, Pantoprazole, Sucralfate
References
- 1.
- He B, Carleton B, Etminan M. Risk of gynecomastia with users of proton pump inhibitors. Pharmacotherapy. 2019;39:614–8. [PubMed: 30865318]
- 2.
- Carvajal A, Macias D, Gutierrez A, et al. Gynaecomastia associated with proton pump inhibitors: A case series from the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System. Drug Saf. 2007;30:527–31. [PubMed: 17536878]
- 3.
- Ashfaq M, Haroon MZ, Alkahraman YM. Proton pump inhibitors therapy and risk of hyperprolactinemia with associated sexual disorders. Endocr Regul. 2022;56:134–47. [PubMed: 35489049]
- 4.
- Patrascu OM, Chopra D, Dwivedi S. Galactorrhoea: Report of two cases. Maedica (Bucur). 2015;10:136–9. [PMC free article: PMC5327809] [PubMed: 28275406]
Substance Identification
Substance Name
Rabeprazole
CAS Registry Number
117976-89-3
Drug Class
Breast Feeding
Lactation
Milk, Human
Anti-Ulcer Agents
Gastrointestinal Agents
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Disclaimer: Information presented in this database is not meant as a substitute for professional judgment. You should consult your healthcare provider for breastfeeding advice related to your particular situation. The U.S. government does not warrant or assume any liability or responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of the information on this Site.
Publication Details
Publication History
Last Revision: May 15, 2022.
Copyright
Attribution Statement: LactMed is a registered trademark of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Publisher
National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, Bethesda (MD)
NLM Citation
Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2006-. Rabeprazole. [Updated 2022 May 15].