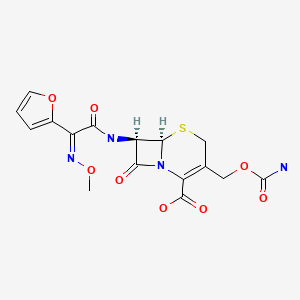
CASRN: 55268-75-2
Drug Levels and Effects
Summary of Use during Lactation
Limited information indicates that cefuroxime produces low levels in milk that are not expected to cause severe adverse effects in breastfed infants. Cefuroxime does not appear to alter the flora of breastmilk when used alone, but it can alter the infant’s fecal flora.[1] Occasionally, diarrhea or thrush have been reported with cephalosporins, but these effects have not been adequately evaluated. Cefuroxime is acceptable in nursing mothers.
Drug Levels
Maternal Levels. A single intravenous dose of 750 mg of cefuroxime was given to 5 women. The average peak cefuroxime level in milk was 0.37 mg/L 3 hours after the dose. Individual peak levels of 0.33 to 0.5 mg/L occurred 2 to 4 hours after the dose.[2]
A single intramuscular injection of 750 mg of cefuroxime was given to 8 women with endometritis. Milk cefuroxime levels increased from 0.34 mg/L at 30 minutes after the injection to 1.45 mg/L at 8 hours after the injection.[3]
After cefuroxime 750 mg three times daily intramuscularly, peak milk levels averaging 1.2 mg/L occurred 6 hours after the dose. Cefuroxime was detectable at a concentration of 0.36 mg/L 30 minutes after the dose, and by 8 hours the milk level had decreased to 1.06 mg/L.[4]
One mother received cefuroxime axetil 500 mg orally three times daily for acute mastitis of the left breast following incision and drainage of the lesion. Milk samples were taken from each breast 30 minutes after the dose on day 1 of therapy. The concentration of cefuroxime in the unaffected breast was 90 mcg/L and the concentration in the breast treated for mastitis was 590 mcg/L. On day 2 of therapy, milk samples from the right and left breast were taken 90 minutes after the dose were 57 and 59 mcg/L, respectively. On day 3, milk samples obtained 90 minutes after the dose contained 27 mcg/L in the unaffected breast and 1.07 mg/L in the affected breast.[5]
Two women were who had been receiving intravenous cefuroxime 750 mg 3 times daily for 2 days following cesarean section donated milk samples 1 hours after the dose. Milk concentrations were 0.34 and 0.39 mg/L.[6]
Two women who had just stopped breastfeeding each took a single 500 mg dose or oral cefuroxime axetil. Ten milk samples collected over 24 hours found peak milk concentrations of 618.9 and 685.3 mcg/L at 4 hours after the dose. At 24 hours after the dose, the milk concentration were 28.6 and 26.4 mcg/L.[7]
Infant Levels. Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects in Breastfed Infants
A prospective, controlled study asked mothers who called an information service about adverse reactions experience by their breastfed infants. Mothers were taking either cephalexin or cefuroxime. No statistical difference was found in the rate of adverse reactions in the 2 groups, with 1 case of diarrhea in each. This amounted to 2.6% of the cefuroxime-exposed infants.[8]
Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
References
- 1.
- Ji C, Zhang G, Xu S, et al. Antibiotic treatments to mothers during the perinatal period leaving hidden trouble on infants. Eur J Pediatr 2022;181:3459-71. [PMC free article: PMC9395442] [PubMed: 35680662]
- 2.
- Takase Z, Shirofuji H, Uchida M. Fundamental and clinical studies of cefuroxime in the field of obstetrics and gynecology. Chemotherapy (Tokyo) 1979;27 (Suppl 6):600-2.
- 3.
- Voropaeva SD, Emelyanova AI, Ankirskaya AS, et al. [Effectiveness of using cefuroxime in the obstetrics and gynecology clinic]. Antibiotiki 1982;27:697-701. [PubMed: 7149693]
- 4.
- Amiraslanova LA, Emel'yanova AI, Fursova SA, Rukhadze TG. [Some aspects of ampicillin, kanamycin and cefuroxim pharmacokinetics in puerperant patients with endometritis]. Akush Ginekol (Mosk) 1985;10 14-7. [PubMed: 2934996]
- 5.
- Nakamura T, Hashimoto I, Sawada Y, Mikami J. [Clinical studies on cefuroxime axetil in acute mastitis]. Jpn J Antibiot 1987;40:340-8. [PubMed: 3599383]
- 6.
- Kiriazopoulos E, Zaharaki S, Vonaparti A, et al. Quantification of three beta-lactam antibiotics in breast milk and human plasma by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography/positive-ion electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Drug Test Anal 2017;9:1062-72. [PubMed: 27714984]
- 7.
- Kul A, Sagirli O. Determination of cefuroxime in breast milk by LC-MS/MS using SALLME technique. Biomed Chromatogr 2023:e5744. [PubMed: 37698043]
- 8.
- Benyamini L, Merlob P, Stahl B, et al. The safety of amoxicillin/clavulanic acid and cefuroxime during lactation. Ther Drug Monit 2005;27:499-502. [PubMed: 16044108]
Substance Identification
Substance Name
Cefuroxime
CAS Registry Number
55268-75-2
Drug Class
Breast Feeding
Lactation
Milk, Human
Anti-Infective Agents
Antibacterial Agents
Cephalosporins
Disclaimer: Information presented in this database is not meant as a substitute for professional judgment. You should consult your healthcare provider for breastfeeding advice related to your particular situation. The U.S. government does not warrant or assume any liability or responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of the information on this Site.
Publication Details
Publication History
Last Revision: November 15, 2023.
Copyright
Attribution Statement: LactMed is a registered trademark of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Publisher
National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, Bethesda (MD)
NLM Citation
Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2006-. Cefuroxime. [Updated 2023 Nov 15].