NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet].
Show detailsOVERVIEW
Introduction
Quazepam is an orally available benzodiazepine used to treat insomnia. As with most benzodiazepines, quazepam has not been associated with serum aminotransferase or alkaline phosphatase elevations during therapy, and clinically apparent liver injury from quazepam has not been reported and must be very rare, if it occurs at all.
Background
Quazepam (quazepam) is a benzodiazepine used as a sleeping aid in the therapy of insomnia. The antianxiety (anxiolytic) and soporific activity of the benzodiazepines is mediated by their ability to enhance gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) mediated inhibition of synaptic transmission through binding to the GABA A receptor. Quazepam was approved in the United States in 2007, but is now not commonly used, having been replaced by non-benzodiazepines that bind to the benzodiazepine receptor on the GABA-A receptor complex, which have a shorter duration of action and are better tolerated. Quazepam is available in capsules and tablets 15 mg generically and under the brand name Doral. The recommended initial oral dose for adults is 15 mg at bedtime, which can be decreased to 7.5 mg nightly. Quazepam is recommended only for temporary therapy of insomnia and not as chronic therapy. The most common side effects are dose related and include daytime drowsiness, lethargy, ataxia, dysarthria and dizziness. Tolerance develops to these side effects, but tolerance may also develop to the effects on insomnia. Quazepam like all oral benzodiazepines has a boxed warning in its product label stressing (1) the risks of severe sedation and potentially fatal respiratory depression when combined with opiates, (2) with prolonged use, the risks of abuse, misuse, and addiction which can lead to overdose and death, and (3) with continued use, the risks of dependence and severe life-threatening withdrawal symptoms if discontinued suddenly.
Hepatotoxicity
Quazepam, like other benzodiazepines, is rarely associated with serum ALT or alkaline phosphatase elevations, and clinically apparent liver injury from quazepam is extremely rare, if it occurs at all. There have been no case reports of symptomatic, acute liver injury from quazepam, but it has not had extensive use. Isolated single cases of clinically apparent liver injury have been reported with other benzodiazepines including alprazolam, chlordiazepoxide, clonazepam, diazepam, flurazepam, lorazepam, and triazolam. The clinical pattern of acute liver injury from benzodiazepines is typically cholestatic and mild-to-moderate in severity with a latency of 1 to 6 months and recovery within 1 to 2 months of stopping. Fever and rash are uncommon as is autoantibody formation.
Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury).
Mechanism of Injury
Quazepam is metabolized by the liver to inactive metabolites and excreted in the urine. Liver injury from benzodiazepines is probably due to the toxic effects of a rarely produced intermediate metabolite.
Outcome and Management
The case reports of hepatic injury due to benzodiazepines were followed by prompt and complete recovery upon stopping the medication, without evidence of residual or chronic injury. No cases of acute liver failure or chronic liver injury due to quazepam have been described. There is no information about cross reactivity with other benzodiazepines, but some degree of cross sensitivity may occur.
Drug Class: Sedatives and Hypnotics, Benzodiazepines
PRODUCT INFORMATION
REPRESENTATIVE TRADE NAMES
Quazepam – Generic, Doral®
DRUG CLASS
Sedatives and Hypnotics
Product labeling at DailyMed, National Library of Medicine, NIH
CHEMICAL FORMULA AND STRUCTURE
| DRUG | CAS REGISTRY NUMBER | MOLECULAR FORMULA | STRUCTURE |
|---|---|---|---|
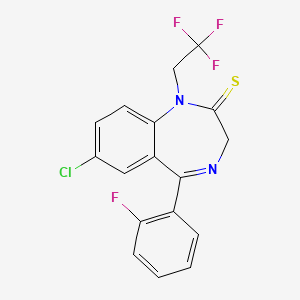
| Quazepam | 36735-22-5 | C17-H11-Cl-F4-N2-S |
|
ANNOTATED BIBLIOGRAPHY
References updated: 22 June 2023
- Zimmerman HJ. Benzodiazepines. Psychotropic and anticonvulsant agents. In, Zimmerman HJ. Hepatotoxicity: the adverse effects of drugs and other chemicals on the liver. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott, 1999, pp. 491-3.(Expert review of benzodiazepines and liver injury published in 1999; mentions rare instances of cholestatic hepatitis have been reported due to alprazolam, chlordiazepoxide, diazepam, flurazepam, and triazolam, and hepatocellular injury with clorazepate and clotiazepam, but no reports of hepatic injury with lorazepam, oxazepam, or temazepam).
- Larrey D, Ripault MP. Anxiolytic agents. Hepatotoxicity of psychotropic drugs and drugs of abuse. In, Kaplowitz N, DeLeve LD, eds. Drug-induced liver disease. 3rd ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2013, p. 455.(Review of sedative induced liver injury mentions that rare instances of acute liver injury [usually cholestatic] have been reported with alprazolam, bentazepam, clotiazepam, chlordiazepoxide, diazepam, flurazepam, and triazolam; a hepatitis-like pattern has been reported with clonazepam and clorazepate).
- Mihic SJ, Mayfield J, Harris RA. Hypnotics and sedatives. In, Brunton LL, Hilal-Dandan R, Knollman BC, eds. Goodman & Gilman’s the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. 13th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2018, pp. 339-53.(Textbook of pharmacology and therapeutics).
- Davion T, Capron-Chivrac D, Andrejak M, Capron JP. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1985;9:117–26. [Hepatitis due to antiepileptic agents] [PubMed: 3920108](Review of hepatotoxicity of anticonvulsants; among benzodiazepines, cases of cholestatic hepatitis have been linked to chlordiazepoxide and diazepam, but liver injury from this class of drugs is exceptionally rare).
- Lewis JH, Zimmerman HJ. Drug- and chemical-induced cholestasis. Clin Liver Dis. 1999;3:433–64. vii. Erratum in: Clin Liver Dis 1999; 3: 917. [PubMed: 11291233](Review of drug induced cholestatic syndromes, listing many causes including chlordiazepoxide and flurazepam; “Benzodiazepines may cause cholestatic injury, although this is rare”).
- Sabaté M, Ibáñez L, Pérez E, Vidal X, Buti M, Xiol X, Mas A, et al. Risk of acute liver injury associated with the use of drugs: a multicentre population survey. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007;25:1401–9. [PubMed: 17539979](Among 126 cases of drug induced liver injury seen in Spain between 1993-2000, 20 were attributed to benzodiazepines including 5 for clorazepate, 5 alprazolam, 6 lorazepam, and 4 diazepam, but compared to controls, relative risk of injury was increased only for clorazepate [8.3: estimated frequency 3.4 per 100,000 person-year exposures]).
- Chalasani N, Fontana RJ, Bonkovsky HL, Watkins PB, Davern T, Serrano J, Yang H, Rochon J., Drug Induced Liver Injury Network (DILIN). Causes, clinical features, and outcomes from a prospective study of drug-induced liver injury in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:1924–34. [PMC free article: PMC3654244] [PubMed: 18955056](Among 300 cases of drug induced liver disease in the US collected from 2004 to 2008, none were attributed to a benzodiazepine).
- Björnsson E. Hepatotoxicity associated with antiepileptic drugs. Acta Neurol Scand. 2008;118:281–90. [PubMed: 18341684](Review of hepatotoxicity of all anticonvulsants focusing upon phenytoin, valproate, carbamazepine; “Furthermore, hepatoxicity has not been convincingly shown to be associated with the use of benzodiazepines”).
- Reuben A, Koch DG, Lee WM., Acute Liver Failure Study Group. Drug-induced acute liver failure: results of a U.S. multicenter, prospective study. Hepatology. 2010;52:2065–76. [PMC free article: PMC3992250] [PubMed: 20949552](Among 1198 patients with acute liver failure enrolled in a US prospective study between 1998 and 2007, 133 were attributed to drug induced liver injury, but none were attributed to a benzodiazepine).
- Drugs for insomnia. Treat Guidel Med Lett. 2012;10(119):57–60. [PubMed: 22777275](Guidelines for therapy of insomnia mentions that benzodiazepines are controlled substances and, when used for sleep, may impair next day performance).
- Björnsson ES, Bergmann OM, Björnsson HK, Kvaran RB, Olafsson S. Incidence, presentation and outcomes in patients with drug-induced liver injury in the general population of Iceland. Gastroenterology. 2013;144:1419–25. [PubMed: 23419359](In a population based study of drug induced liver injury from Iceland, 96 cases were identified over a 2 year period, but none were attributed to quazepam or any other benzodiazepine, despite the fact millions of prescriptions for them are filled yearly).
- Hernández N, Bessone F, Sánchez A, di Pace M, Brahm J, Zapata R, A, Chirino R, et al. Profile of idiosyncratic drug induced liver injury in Latin America. An analysis of published reports. Ann Hepatol. 2014;13:231–9. [PubMed: 24552865](Systematic review of literature on drug induced liver injury in Latin American countries published from 1996 to 2012 identified 176 cases, none of which were attributed to a benzodiazepine).
- Chalasani N, Bonkovsky HL, Fontana R, Lee W, Stolz A, Talwalkar J, Reddy KR, et al. United States Drug Induced Liver Injury Network. Features and outcomes of 899 patients with drug-induced liver injury: The DILIN Prospective Study. Gastroenterology. 2015;148:1340–1352.e7. [PMC free article: PMC4446235] [PubMed: 25754159](Among 899 cases of drug induced liver injury enrolled in a US prospective study between 2004 and 2013, no cases were attributed to quazepam or any other benzodiazepine).
- Drugs for chronic insomnia. Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2023;65:1–6. [PubMed: 36630579](Concise review of drugs for chronic insomnia mentions that tolerance and dependence can occur with use of benzodiazepines and their use should be discouraged, and that benzodiazepines are CNS suppressants and can impair next day performance including driving and cause complex behavior disorders, retrograde amnesia, dependence, tolerance, abuse and rebound insomnia; no mention of ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity).
- PMCPubMed Central citations
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- PubMedLinks to PubMed
- Review Estazolam.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Estazolam.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Review Temazepam.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Temazepam.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Review Flurazepam.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Flurazepam.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Review Triazolam.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Triazolam.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Insomnia in generalized anxiety disorder: polysomnographic, psychometric and clinical investigations before, during and after therapy with a long- versus a short-half-life benzodiazepine (quazepam versus triazolam).[Neuropsychobiology. 1994]Insomnia in generalized anxiety disorder: polysomnographic, psychometric and clinical investigations before, during and after therapy with a long- versus a short-half-life benzodiazepine (quazepam versus triazolam).Saletu B, Anderer P, Brandstätter N, Frey R, Grünberger J, Klösch G, Mandl M, Wetter T, Zeitlhofer J. Neuropsychobiology. 1994; 29(2):69-90.
- Quazepam - LiverToxQuazepam - LiverTox
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...